The engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT sensor) is one of the most important parts of a car’s engine management system. It constantly monitors the temperature of the engine’s coolant and sends signals to the car’s computer (ECU). This allows the engine to maintain the right temperature for performance, efficiency, and safety.
Without a properly working coolant temperature sensor, your car may experience problems like poor fuel economy, hard starts, overheating, or even engine damage. Understanding how this sensor works, what symptoms show when it fails, and how to maintain it can save you time and money in the long run.
Table of Contents
What is an Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor?
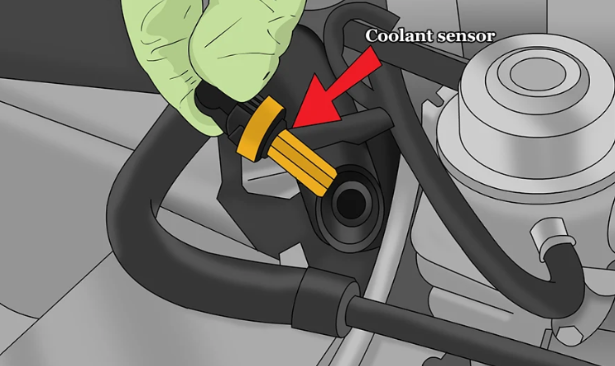
An engine coolant temperature sensor is a small device, usually located near the thermostat or cylinder head, that measures the heat of the coolant. Coolant is the liquid that flows through the engine to keep it from getting too hot.
The sensor contains a thermistor, which is a resistor that changes resistance based on temperature. When the coolant is cold, the resistance is high. As the coolant heats up, the resistance drops. The car’s ECU reads these changes and adjusts things like fuel injection and ignition timing.
In short, the sensor acts as the car’s thermometer, ensuring the engine always runs at an ideal temperature.
How Does the Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Work?
The working principle of the ECT sensor is simple but critical:
- Coolant Heat Detection – As the engine runs, the coolant absorbs heat. The sensor detects this rising temperature.
- Resistance Change – Inside the sensor, the thermistor changes resistance depending on the coolant’s heat.
- Signal to ECU – The ECU (Engine Control Unit) receives the electrical signal from the sensor.
- Adjustments Made – Based on the signal, the ECU adjusts fuel-air mixture, ignition timing, and even cooling fan speed.
For example, during a cold start, the ECU injects more fuel to help the engine warm up quickly. When the engine is hot, the ECU reduces fuel to avoid overheating and improve fuel efficiency.
Signs of a Bad Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
When the ECT sensor goes bad, the car may act strangely because the ECU is getting the wrong information. Some common symptoms include:
- Poor Fuel Economy – The ECU may think the engine is always cold and add extra fuel.
- Hard Starting – The engine may crank too long before starting.
- Check Engine Light – A faulty sensor often triggers the warning light.
- Overheating – The radiator fan may not turn on when needed.
- Black Smoke from Exhaust – Too much fuel can cause unburned fuel to leave the exhaust.
- Erratic Temperature Gauge – The dashboard gauge may show unusual or incorrect readings.
If you notice these signs, it’s important to diagnose the sensor quickly to avoid costly engine damage.
Causes of Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Failure
Like any other part, the coolant temperature sensor can fail over time. The most common reasons are:
- Corrosion – Exposure to coolant and moisture can corrode the sensor.
- Wiring Issues – Damaged wires or loose connections may give false readings.
- Coolant Leaks – If coolant is low or leaking, the sensor may not measure correctly.
- Age and Wear – Over years of use, the sensor may simply stop working properly.
How to Test an Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
If you suspect your ECT sensor is faulty, you can test it in a few steps:
- Visual Inspection – Check for corrosion, coolant leaks, or damaged wiring.
- Multimeter Test – Measure the resistance across the sensor terminals. Compare it with manufacturer specifications.
- Scan Tool Check – Use an OBD-II scanner to see if the ECU is getting correct readings.
If the readings are off, replacement is often the best solution.
Replacing an Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Replacing an ECT sensor is usually simple and inexpensive. Here’s the general process:
- Turn Off Engine – Make sure the engine is cool to avoid burns.
- Locate Sensor – Usually found near the thermostat housing or cylinder head.
- Disconnect Wiring Harness – Carefully unplug the connector.
- Remove Sensor – Use a wrench to unscrew the sensor.
- Install New Sensor – Screw in the new one and reconnect the harness.
- Check Coolant Level – Top up if needed.
- Test – Start the car and check if the issue is resolved.
Most replacement sensors cost between $20 and $100, making it a relatively affordable repair.
Importance of Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor in Modern Cars
Modern cars rely heavily on electronic sensors. The ECT sensor not only controls engine performance but also plays a role in:
- Emissions Control – Prevents too much unburned fuel from polluting the air.
- Cooling System Operation – Activates the radiator fan when needed.
- Fuel Injection Control – Adjusts mixture for better efficiency.
- Dashboard Gauges – Ensures you see the correct temperature reading.
Without a properly working sensor, the whole system may fail to operate smoothly.
Preventive Maintenance for ECT Sensors
While sensors can fail naturally, you can extend their life with good maintenance:
- Regularly check coolant levels.
- Flush and replace coolant as recommended.
- Inspect wiring for wear or corrosion.
- Fix coolant leaks quickly.
- Don’t ignore a check engine light.
Proper maintenance helps the sensor function correctly and keeps your engine safe.
Conclusion
The engine coolant temperature sensor may be small, but it plays a big role in your car’s health. It ensures your engine runs smoothly, saves fuel, prevents overheating, and reduces harmful emissions. A faulty sensor can cause poor performance, high fuel use, and even engine damage.
By recognizing the signs of a bad sensor, testing it properly, and replacing it when needed, you can avoid bigger and costlier repairs. Keeping your ECT sensor in good shape means keeping your car reliable on the road.
FAQs
Q1: What happens if I drive with a bad coolant temperature sensor?
Driving with a bad sensor can lead to overheating, poor fuel economy, and engine damage. It’s best to replace it as soon as possible.
Q2: How much does it cost to replace an engine coolant temperature sensor?
On average, the part costs $20–$100, and labor can add another $50–$150 depending on your car.
Q3: Can a bad coolant temperature sensor cause overheating?
Yes. If the fan doesn’t turn on at the right time due to false readings, the engine may overheat.







